Uxio Fernandez Hermo, one of our SAP consultants, conducted a webinar on the Introduction to SAP IAG. How does it differ from SAP GRC Access Control? The webinar was held on our partner platform CUVIV and consisted of two one-hour sessions. One session was scheduled in the morning for the European audience, while the other took place in the afternoon for the Latin American audience.
Targeted towards users with some knowledge of SAP, this webinar aimed to expand their knowledge and facilitate interaction with Uxio at the end of each session.
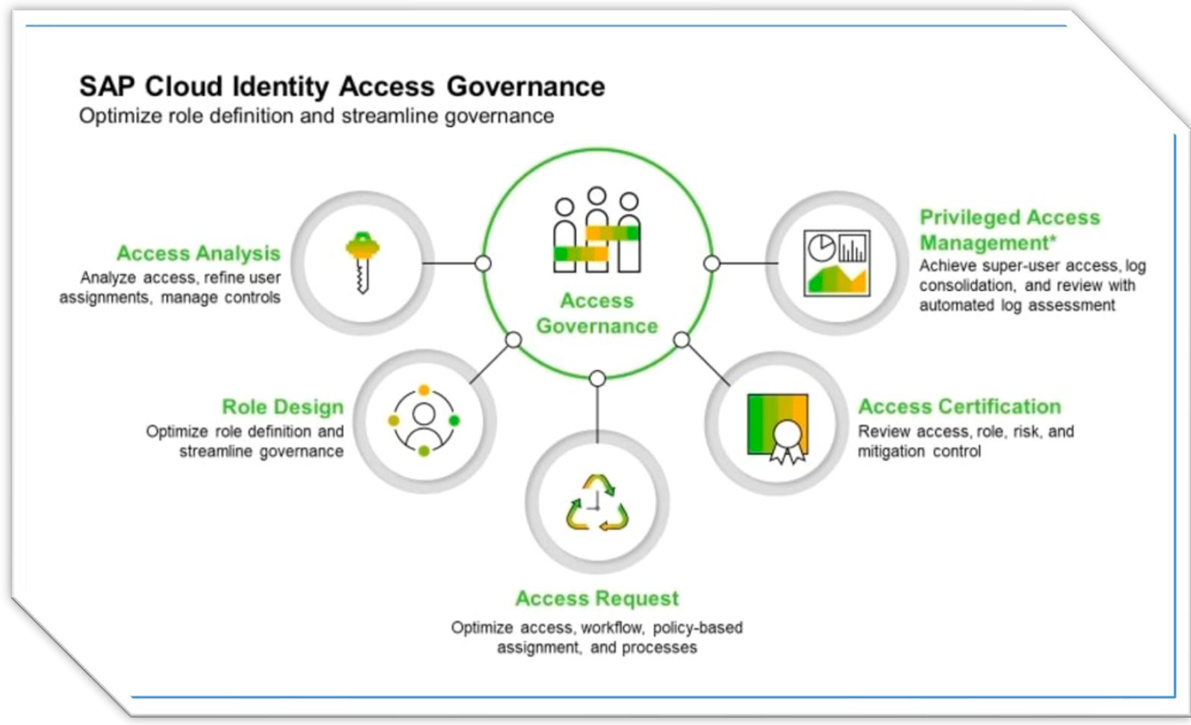
SAP IAG Features
During the presentation, Uxio delved into Access Analysis Service, a service that functions similarly to Access Risk Analysis in SAP GRC AC, enabling the management of risks in systems connected to IAG. He explained the main differences compared to GRC AC, highlighting the native risk analysis for Cloud systems (AC only allows it for SuccessFactors) and the ability to perform cross-system risk analysis between both Cloud and non-Cloud applications.
He emphasized the advantages of tools like Privilege Access Management (PAM), which allows for the management of emergency access from request to review. PAM integrates with Access Request Service, enabling the request of emergency access through an approval workflow. When properly configured, this tool can be used directly by end-users without the need for administrative intervention. Uxio pointed out differences from GRC AC, such as its use only in ABAP systems, reliance on ID-based emergency access, and decentralized usage. Additionally, PAM doesn’t require software installation on satellite systems; ABAP is sufficient.
Uxio then analyzed the functionalities of Access Request Service. This tool centralizes access management in SAP, using an approval workflow that enhances efficiency and traceability of changes. Unlike GRC AC, the workflows are not as configurable. Key differences from GRC AC include the ability to connect with both On-Premise and Cloud systems. Furthermore, HR events can be integrated to automate the Hire to Retire process, which cannot be customized in IAG as extensively as in GRC AC.
Lastly, within the IAG functionalities, there’s Role Design Service, which manages the lifecycle of SAP system roles. It serves as a repository for roles that can be added to access requests through the Access Request service.
It differs from GRC AC in that it can be used as a repository for both On-Premise and Cloud system roles, providing assistants that assist administrators in creating Business Roles and also requiring less information for role categorization.
Integrations
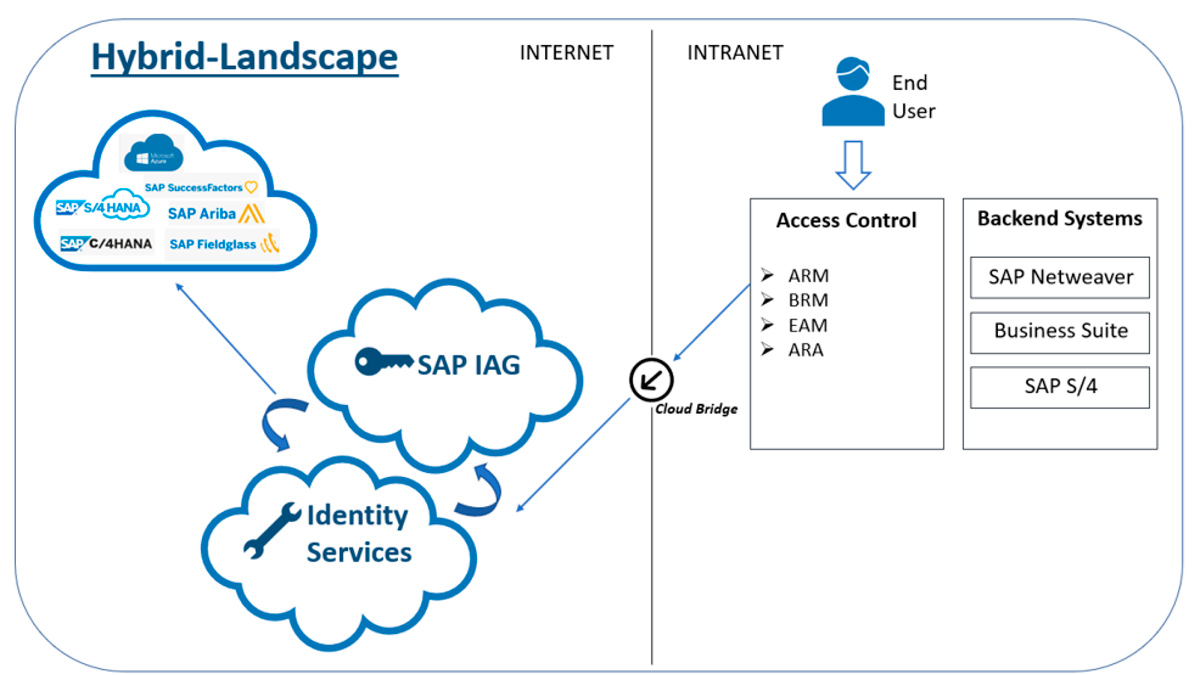
When to Implement GRC AC or IAG?
IAG-Only Scenario: In this scenario, companies would use IAG as the sole access control application.
Hybrid Scenario (GRC AC + IAG): In this scenario, SAP GRC AC is used for access management, and through a native integration with SAP GRC AC, IAG handles tasks related to Cloud systems. This scenario includes risk analysis, emergency access, access requests, and role management.
Conclusions
As shown throughout this article, the best outcome can be achieved by using the hybrid scenario in which SAP GRC AC and SAP IAG work together. The choice between a purely Cloud model (IAG only), a mixed model (IAG & GRC AC), or a purely On-Premise model (GRC AC) can be summarized as follows:
- Cloud Solution: Suitable for organizations with fewer than 500 users or straightforward and standardized access control processes, especially those related to account management. It can easily adapt to default processes provided by SAP IAG, and when access control over Cloud-type systems is needed. It’s worth noting that the licensing cost of SAP IAG is lower than SAP GRC AC.
- Hybrid Solution: Recommended for organizations with more than 500 users or complex processes. If an organization needs to manage access to Cloud systems and requires a high degree of customization in the tool, this solution is suitable. GRC AC offers greater adaptability, and when used in conjunction with SAP IAG, it can extend its capabilities to Cloud systems.
- On-Premise Solution: If an organization has more than 500 users and does not need to manage access to Cloud systems, implementing only SAP GRC AC would be advisable.