In this article, we will review the features SAP® offers to make the GRC system available in different languages. It is important to understand that, from a global perspective, a single language for the entire organization should be used. However, this might reduce your ROI (Return on Investment) regarding the SAP® GRC license. Having fewer stakeholders due to a lack of knowledge of the organization’s global language could impact local procedures that could be integrated into SAP® GRC.
Languages Available in SAP®GRC
SAP® provides, as part of the SAP® GRC license, different languages that can be used by any organization:
- Afrikaans; Arabic; Bulgarian; Catalan; Chinese; Traditional Chinese; Croatian; Czech; Danish; Dutch; English; Estonian; Finnish; French; German; Greek; Hebrew; Hungarian; Icelandic; Indonesian; Italian; Japanese; Korean; Latvian; Lithuanian; Malay; Norwegian; Polish; Portuguese; Romanian; Russian; Serbian; Serbo-Croatian; Slovak; Slovenian; Spanish; Swedish; Thai; Turkish; Ukrainian
As with any decision, there are pros and cons that must be considered, and it is important to analyze the business case for this option for each organization. If the decision remains to implement a multilingual environment for SAP® GRC, you will find that the standard SAP® translation is not perfect and therefore some changes will be required to offer the best solution for end users. In this article, we will review the standard options available within SAP® GRC.
Direct Change in NWBC
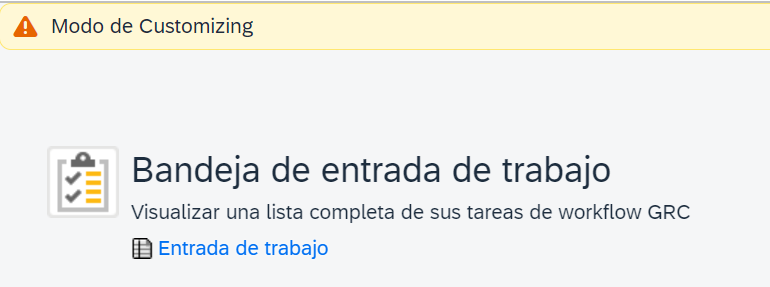
This is the option GRC consultants use many times, but it is NOT a translation; it is only a direct change. You can modify any description by activating Customization Mode:
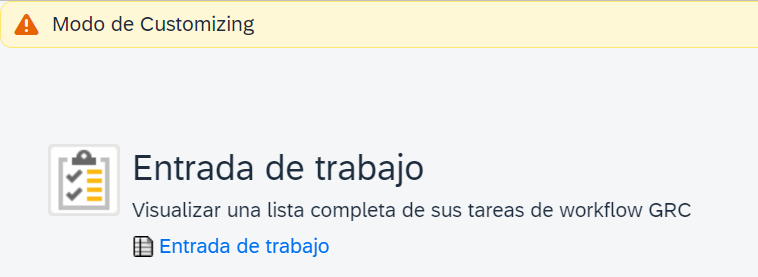
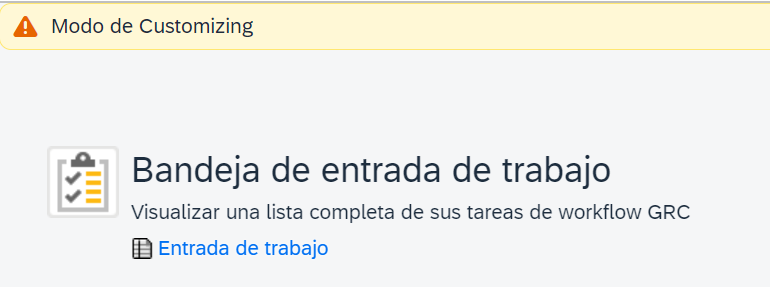
However, if we change the language, we will see the issue that arises with this option (The direct change in Spanish also appears in English and overwrites the English translation):
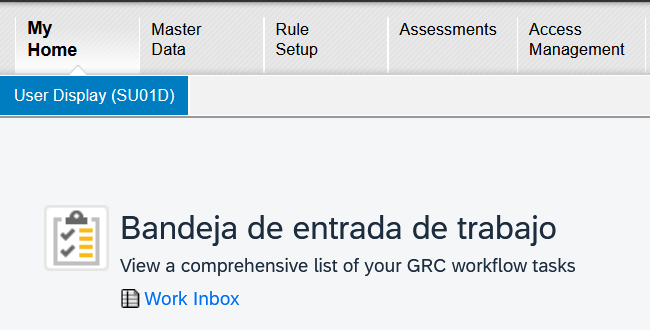
Therefore, it is important to explain that this type of change is not a translation but a direct change within the NWBC/SAP® portal interface.
SE63 Translation
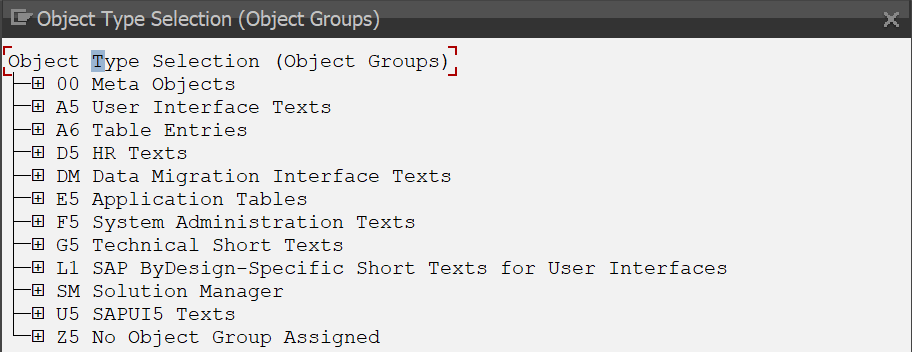
This is the most commonly used transaction for performing translations. You can select different “ABAP Objects”:
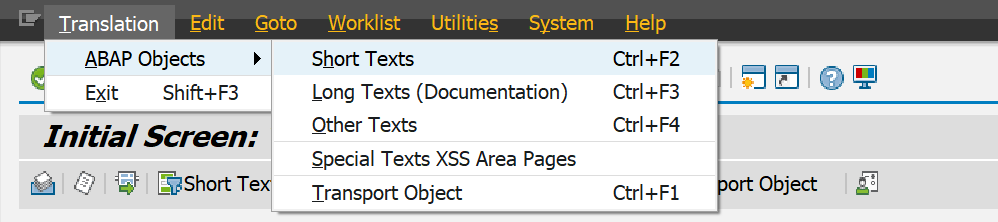
However, the list of available fields is quite extensive, so finding the one you need is a challenge:
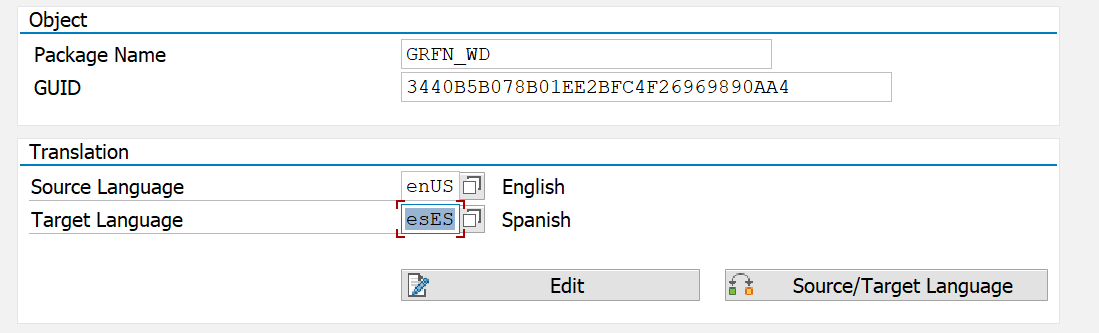
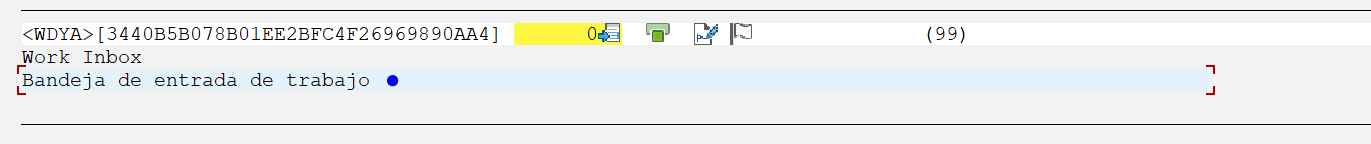
Our recommendation is to use the “SOTR_EDIT” transaction before moving to the SE63 transaction. SOTR_EDIT is very useful for finding the specific field we are looking for. As shown in the previous section, we will change the text of the GRC inbox. Based on the image below, we have the following key fields:
- Package: GRFN_WD
- Concept: 3440B5B078B01EE2BFC4F26969890AA4
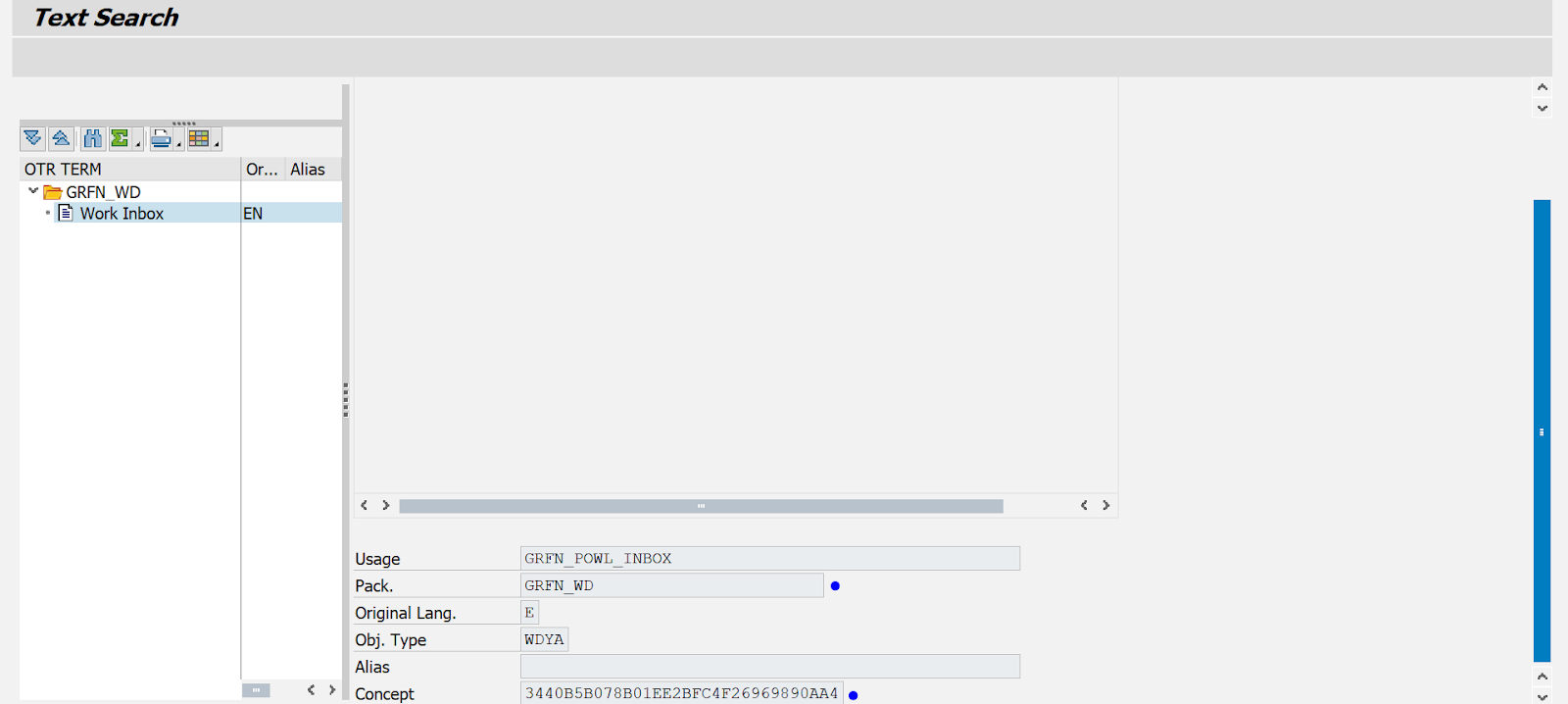
Once the key fields “Package” and “Concept” are identified, we will use them within the SE63 transaction:

SE11 Translation
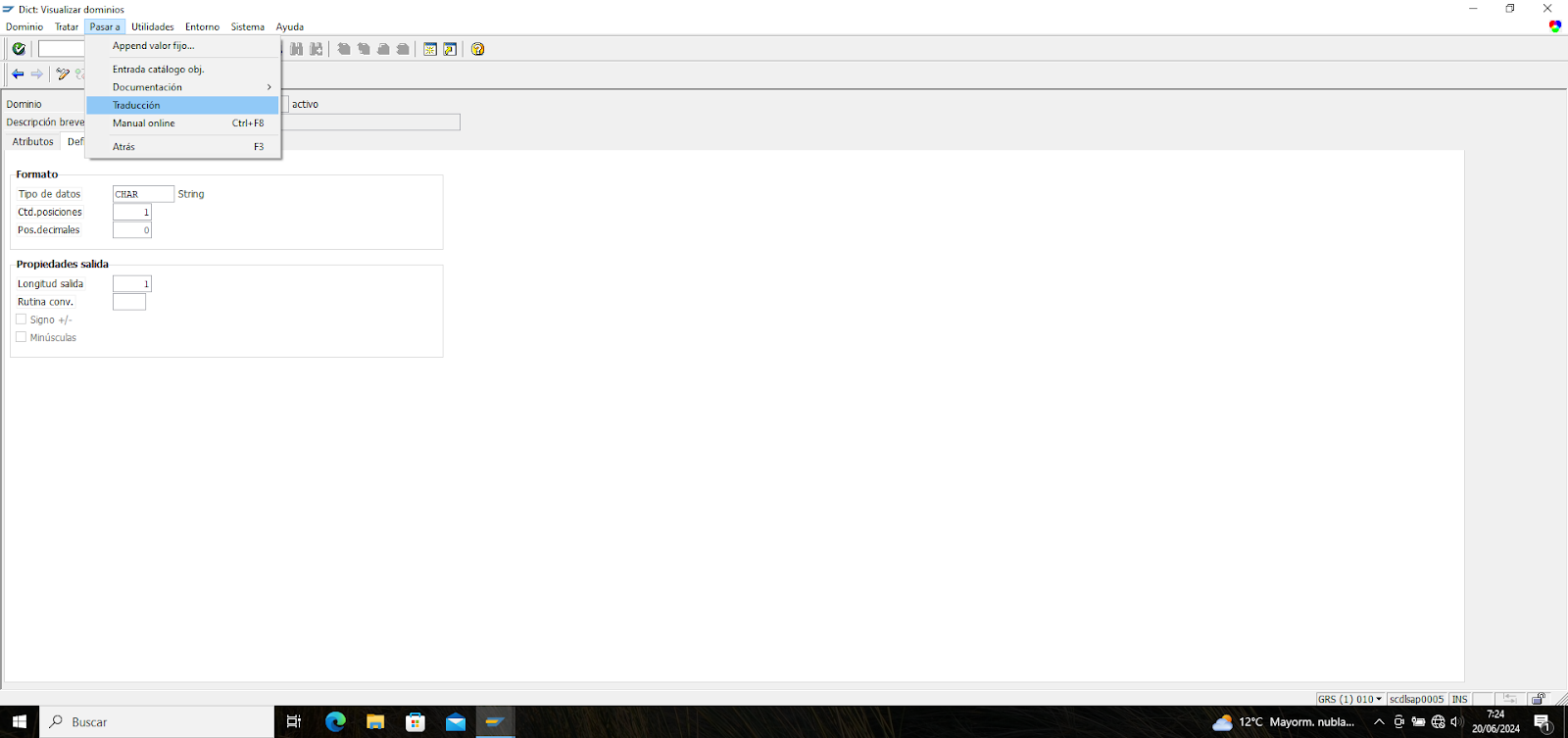
There are cases where the translation you need to perform includes a list of values within a GRC field. This type of translation cannot be done using SE63, and SE11 must be used. The first step is finding the specific field you need to translate, which is the most challenging part because there is no list of all GRC fields and the corresponding technical name of that field. Once you have the technical name of the field, you must access it within SE11 and select “Translation” from the menu at the top of the screen.
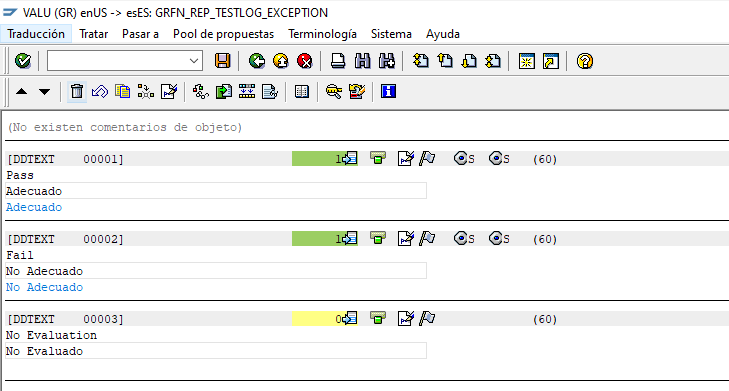
Once in the translation, select the language you would like to change, and you will see the translation included by SAP®, which can be adapted to the values required by your organization:
SPRO Translation
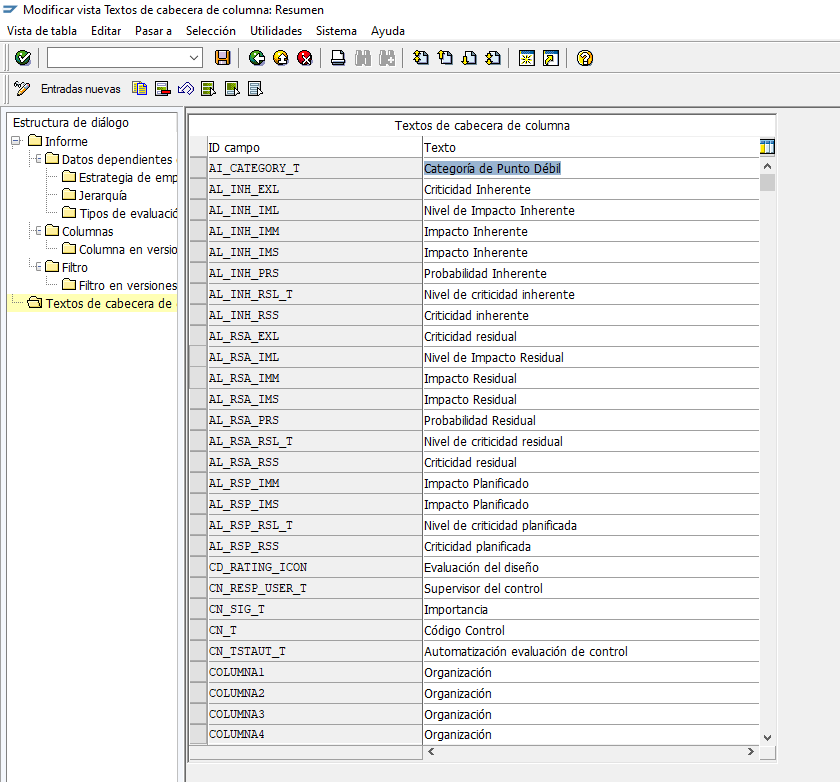
Another option provided by SAP® within the SPRO transaction allows you to adapt the information displayed in SAP® standard reports.
This option lets you view the list of columns used in SAP® GRC standard reports and the corresponding name provided by SAP®. The name is editable, so it can be adapted to the name required by your organization.
Key Points
To summarize, here are the seven key points about multilingual translation in SAP® GRC:
- Having more stakeholders as part of processes integrated into SAP® GRC will increase ROI. However, it is important to understand the pros and cons of this decision.
- DO NOT use NWBC administration access to perform a translation because it is not a translation, but a direct change.
- Use the “SOTR_EDIT” transaction to identify which field requires translation in your organization.
- There are cases where translation cannot be performed through the “SE63” transaction, so “SE11” MUST be used.
- If you need to change the name of columns in SAP® GRC standard reports, there is a standard option within the “SPRO” transaction that can be used (you can also make the change via “SE11,” but it is more difficult to find the appropriate GRC field).
- Once all required translations are completed, you can include them all in a transport request.
- There is an internal prioritization of changes, so, for example, a translation through “SPRO” might overwrite a translation through “SE11.”