Introducing one of the first implementations of SAP® GRC Access Control at VCEAA. In this post, we will detail the configuration of all four modules (ARA – Access Risk Analysis; ARM – Access Request Management; EAM – Emergency Access Management; BRM – Business Role Management).
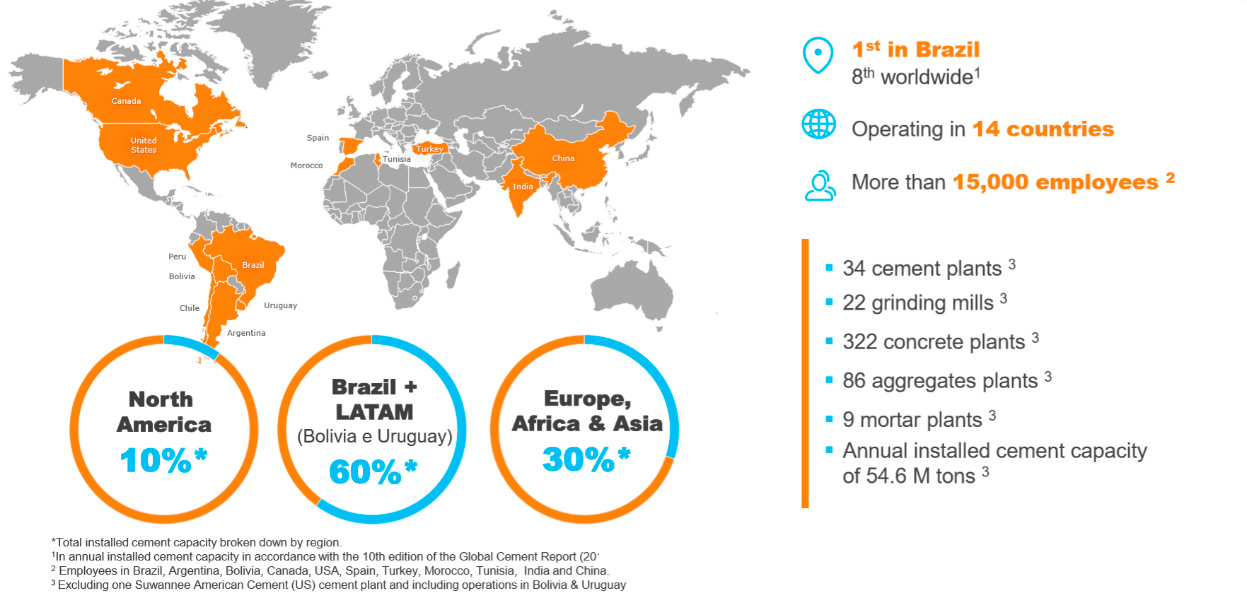
VCEAA is the subsidiary of Votorantim Cimentos in Europe, Africa, and Asia. Votorantim Cimentos is among the top 10 largest cement companies globally.
The Challenge
The challenge in this project stemmed from two different directions. Firstly, the technological aspect, which came from the GRC tool, had a module for Role Management through SAP® GRC that hadn’t been implemented as frequently as other modules. Secondly, there was an organizational aspect where certain processes were not implemented organizationally. A new nomenclature for roles had been developed but wasn’t implemented across all systems. Additionally, the user onboarding, offboarding, and modification process in SAP® needed review to enhance security.
Another challenge was to maximize the return on investment of the SAP® GRC Access Control License by utilizing the full potential of the tool to improve efficiency and security in user access processes within SAP®.
Inprosec Solution
It was decided to expand the functionalities of the existing GRC, which previously only had “Password Self Service” and access provisioning processes in Turkey. This expansion aimed to incorporate the use of EAM and BRM within the VCEAA organization and deploy ARM to the rest of the countries.
Previously, the GRC system had a Segregation of Duties Risk Matrix and a user provisioning process for SAP® in Turkey. Key activities are detailed below:
- Implementation and Deployment of Mitigation Controls (ARA).
- Global Implementation of EAM.
- Global Implementation of ARM.
- Global Implementation of BRM.
ARA – Access Risk Analysis
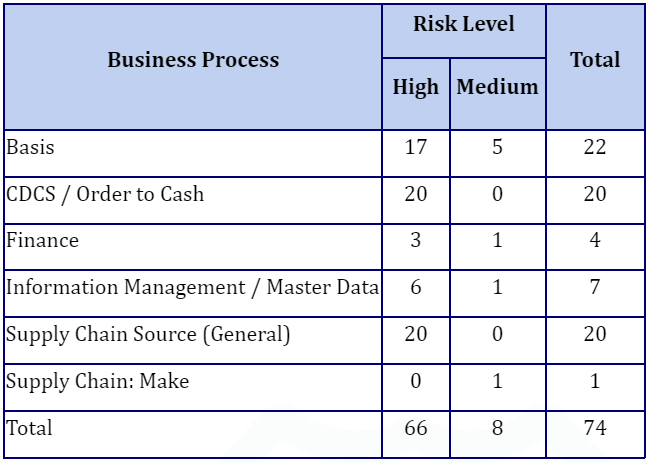
The Access Risk Matrix in SAP® has been updated, expanding its monitoring scope from just 24 Segregation of Duties (SoD) Risks to 46, and additionally incorporating a total of 28 Critical Actions. The final Access Risk Matrix now looks as follows:
Additionally, Z Transactions were added to the Final Access Risk Matrix, which were previously not monitored.
EAM – Emergency Access Management
The entire module was implemented, defining a global emergency access strategy shared across all VCEAA organization countries.
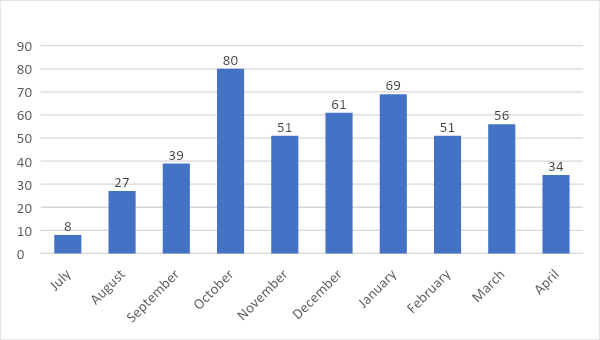
There were 7 different emergency access scenarios, including IT access, SAP® OSS access, Security access, etc.
The Firefighter Log Review Workflow was activated to ensure all accesses and modifications were reviewed.
Statistics were gathered in the initial months, resulting in the following outcomes:
ARM – Access Request Management
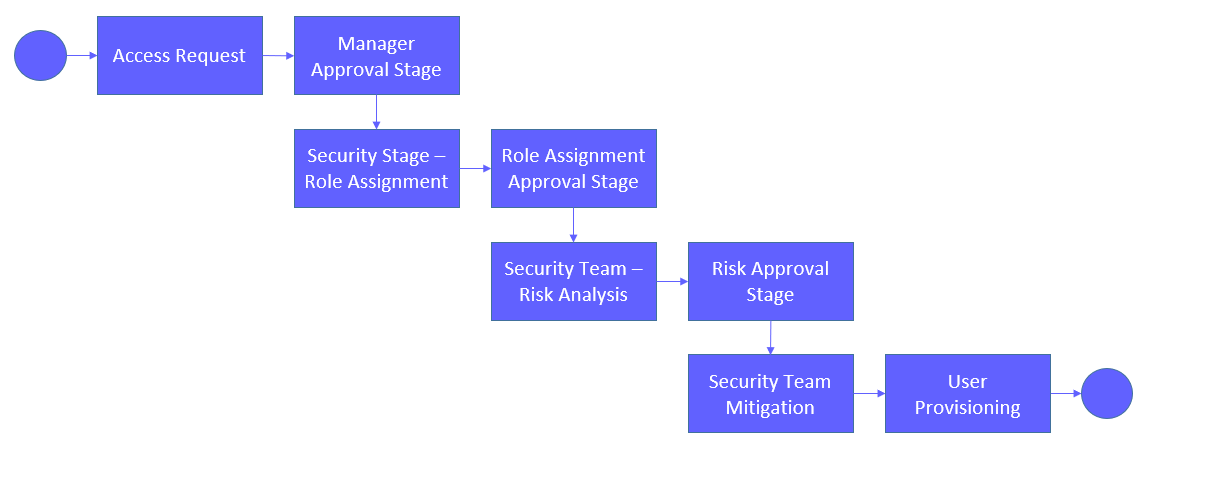
The implementation of the ARM module occurred in parallel with a Role Redesign project to improve the efficiency of the provisioning process. The provisioning process for user additions and modifications was as follows:
Additionally, as part of the ARM module, there was a functionality called “HR Triggers.” This application allowed for the automation of request creation processes based on changes made to the employee master data in SAP® HCM.
The HR Triggers were specifically implemented for the termination process. So, when someone from the HR department recorded a termination, the GRC system automatically generated a request to lock the account in all SAP® systems where it existed.
BRM – Business Role Management
In this case, the challenge was more significant as it required not only a technological project but also the design and implementation of the Role Management process in SAP®. This meant that as the process was designed, the technological implementation of each stage was analyzed to ensure technical feasibility.
A Role Management process was designed to align closely with the Change Management processes of large organizations, ensuring alignment with audit and security compliance requirements. The Role Management process involved positions like “SAP® Security Manager,” “IT Quality Manager,” and “Key User” (confirming user acceptance testing).
Results
All project challenges and objectives were met, significantly increasing the return on investment of the GRC Access Control License. The global perception that the GRC Access Control License only served to analyze Segregation of Duties Risks and Critical Actions was eliminated. This organizational change led to a continuous improvement dynamic, resulting in better system versions over time.
As with any “Case Study” presentation at SAP® GRC events, it’s essential to highlight seven key points:
- Estimate double the time for training.
- This is a key point because it doesn’t matter if the best system in the world is implemented if users don’t know how to use it.
- A communication plan must be created for all project phases.
- It’s important that this communication plan is aligned with the organization’s senior management to create the most favorable atmosphere for a technological project like the implementation of SAP® GRC Access Control.
- Exercise caution with the deployment of EAM; it’s crucial to define a strategy before the technical implementation of the module.
- Be cautious to avoid misuse of Firefighter access as it places an extra burden on log review tasks.
- Implement all available activities in ARM for the account provisioning process in SAP®.
- There are activities that serve for user lock and unlock, which can be useful in your organization.
- If the SAP® HCM system exists, consider implementing HR triggers.
- They significantly reduce effort in tasks related to user terminations in SAP® and enhance the security of the process by involving only the HR department.
- It is recommended to use the standard reporting included in SAP® GRC.
- There are highly visual reports on Access Risks and Provisioning Requests.
- Invest time in understanding how BRM works.
- This tool represents a change from the traditional way of creating and modifying roles in SAP®. It’s essential to understand its benefits and disadvantages to evaluate its implementation in your organization.
Invest time in understanding how BRM works, as it represents a shift from the traditional way of creating and modifying roles in SAP®, and you need to assess its benefits and disadvantages for your organization.