We are pleased to present the first implementation of SAP® GRC Process Control in Campofrío Food Group, mainly focused on the configuration of a series of strategic automatic controls through the SAP GRC Process Control Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) functionality.
Campofrio Food Group is a leader in the processed meat sector in Europe; it produces and sells its products in France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Portugal and Germany, in addition to Spain, and exports to 80 countries through independent distributors.
Campofrio Food Group is a subsidiary of Sigma Alimentos, a producer of processed meats, dairy products and other refrigerated and frozen products, which it markets through well-positioned brands in the markets in which it participates. Sigma operates 68 plants and 144 distribution centers, serving more than 500,000 customers in 18 countries in North, Central and South America, Western Europe and the Caribbean. Sigma currently employs more than 40,000 people.
The Challenge
Campofrio was using the SAP GRC Access Control module to control and monitor access risks in its SAP systems. To extend the functionality of this tool and establish mechanisms to control and monitor business risks, it is proposed to implement the SAP GRC Process Control module. This implementation will include an initial configuration of the tool and the implementation of a pilot in which a series of automatic controls, considered strategic for audits, will be defined and configured.
Inprosec Solution
The proposed implementation of the SAP GRC Process Control tool and the Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) functionality had a production start-up period of 4 months from the beginning of the project.
During the initial phase of the project, we identified two main risks to mitigate:
- Accountability. It is crucial that those responsible for processes and sub-processes within the company acquire knowledge of the tool, as their participation is key to the present and future success of the project.
- Tecnology. To obtain the log of modifications in certain tables, it was necessary to activate the “change log” check, especially in non-standard tables (“Z” tables).
Implementation
After the initial configuration, it is essential to define the Master Data at the level of Business Units, Processes, Sub-processes and Controls, reflecting the Campofrio structure. These Master Data will be registered in SAP GRC Process Control with their specific descriptions and characteristics.
At this point, the 10 controls to be automated through the CCM tool were determined:
- Change of credit to customers.
- Modifications to Purchase Terms after PO is created.
- Supplier bank account Modification review (incl. Payment terms).
- Review Accounting Period Openings.
- Review 3 Way Match changes.
- Inventory Differences.
- Manual Notes
- Purchase Orders opened for a period longer than 6 months
- Modification of Customer Payment Terms.
For each of these automatic controls, the following characteristics were defined:
- Frequency of execution: hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, semi-annually or annually.
- Owner: user who will receive the control alerts (deficiencies) for review.
- Organization and process: it will be necessary to assign it within the organizational structure.
- Definition of control logic: Within the “Process Control” tool there are several types of controls, such as risk analysis, reporting, search for specific values or review of changes in critical fields. In the latter case, it is essential to evaluate what type of changelogging technology is used to execute the control. The following table shows a comparison between the two main types of logs:
| Change Log | Change Documents |
| One control for each table | One control for several tables |
| Activation required | Activated by default |
| Any change in any field of the table is recorded. | Changes are recorded if transactions allow it |
| The creations show the value of the creation of the field. | Creations show the current value of the field |
| Single column to describe the field, the old value and the new value | Field description, old value and new value in separate columns for the modifications |
| It does not display the transaction from which the change was made. | Displays the transaction from which the change was made |
| Simple and limited logical rules (e.g.: it is not possible to delete changes of a certain user in all cases) | Virtually any logic for the operation of the deficiencies can be implemented. |
| Easier maintenance of the rule over time | Adding a new field to the rule requires configuring the control from scratch |
Development and Deployment
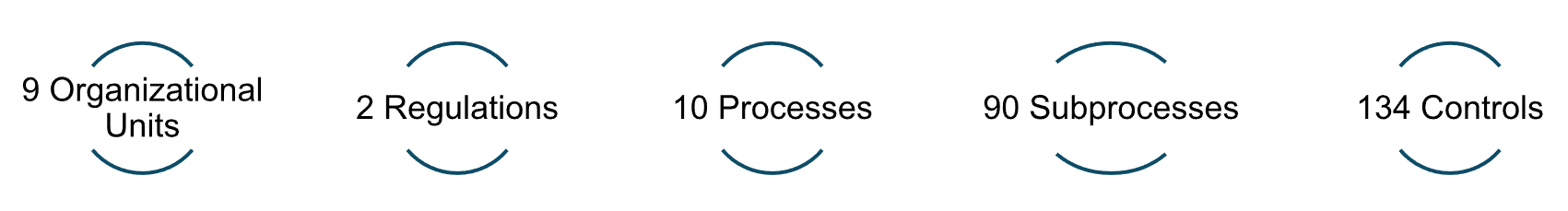
Once the functional design was completed, we proceeded with the technical implementation of the tool, following Campofrío‘s program change management process. This process included the basic configuration, the registration of the organizational structure and the implementation of automatic controls. At the master data level, 9 organizational units, 2 regulations, 10 processes, 90 sub-processes and 134 controls were registered, of which 10 are automated controls through Continuous Control Monitoring, following the matrix defined in Campofrío.
In relation to automated controls, the standard report provided by SAP Control Monitoring History with Ratings was optimized to provide greater visibility of the controls executed and reviewed. A review standard has also been established for each of these automated controls.
The testing phase was then initiated and all documentation related to the tool, both technical and user (control owner) and administrator manuals, were recorded. Specific training sessions were held for each of the controls and an additional session on system administration.
Finally, the production deployment was carried out, scheduling the periodic execution of the automatic controls and starting the support period. During this period, the performance problems that were identified were addressed and the rules were fine-tuned to avoid false positives, ensuring that the controls generated the appropriate alerts.
Deliverables
All deliverables that have been identified in the previous sections are detailed below:
- Biweekly project monitoring report.
- Risk and Controls Matrix.
- Process Control related documentation.
- SAP GRC PC tool configured and running.
- Project Plan.
- Blueprint document with the functional and technical design of the SAP GRC PC tool.
- Training manuals for the use of the SAP GRC PC application.
- Closing report that will include lessons learned and next actions to be recommended.
Results
With the completion of this project, Campofrio has a unique tool that centralizes its matrix of controls and processes, as well as the results of each execution of these controls. It also has its own control review methodology for each owner, thus standardizing this process. It also has an optimized report that provides relevant data at the executive level, allowing real-time visibility of the execution and review of the different controls, facilitating the identification and immediate correction of any non-conformity.
The implementation of SAP GRC Process Control has significantly improved Campofrio‘s ability to control and monitor business risks, establishing a solid foundation for future audits and ensuring ongoing compliance. This translates into less effort, and therefore greater efficiency, when submitting information to audits.